Extrinsic Semiconductors
Extrinsic Semiconductors: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, N-type Semiconductor, Some Important Facts about n-Type Semiconductor, Energy Bands Diagram of N-type Semiconductor & Energy Bands Diagram of P-type Semiconductor etc.
Important Questions on Extrinsic Semiconductors
The diagram below is showing:
Which of the following energy band diagram shows the N-type semiconductor
No crystal is found to be prefect at room temperature. The defects present in the crystals can be stoichiometric or non-stoichiometric. Due to nonstoichiometric defects, the formula of the ionic compound is different from the ideal formula. For example, the ideal formula of ferrous oxide should be but actually in one sample, it was found to be . This is because the crystal may have some ferric ions in place of ferrous ions. These defects change the properties of the crystals. In some cases, defects are introduced to have crystals of desired properties as required in the field of electronics. Doping of elements of Group 14 with those of Group 13 or 15 is most common. In ionic compounds, usually impurities are introduced in which the cation has higher valency than the cation of the parent crystal, e.g., into .
Which one of the following doping will produce p-type semiconductor ?
The hole density and electron density in -type semiconductors are related as
Range of energy required by electron of valance band to move into hole is . The accepter energy level lies
Which of the following energy band diagram shows the N-type semiconductor
The energy gap between conduction band and valence band in semiconductor is
A semiconductor has equal electron and holes concentration of . On doping with certain impurity, electron concentration becomes . Then the semiconductor is
Electric current in extrinsic semiconductor in respect of mobility is expressed as
Electric current in extrinsic semiconductor is
In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true:
In the energy band diagram of material shown below, the open circles and filled circles denote holes and electrons respectively. The material is
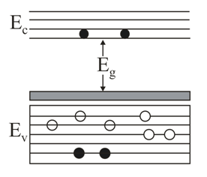
These are the minority charge carriers in n-type semiconductors.
Identify the minority charge carriers in p-type semiconductors
In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true:
Which one of the following doping will produce p-type semiconductor ?

In the above figure, if the in the circled position is replaced by the , then the resultant forms which type of semiconductor?
Which of the following is true regarding -type semiconductor ?
phosphorus atoms and boron atoms are doped in a sample of silicon. If all the dopants are fully ionised, the material is
